Forms of Plagiarism
Name - Himanshi Parmar
Semester - 4 (Four)
Roll Number - 8
Email. Id. - himanshiparmar3004@gmail.com
Enrollment number - 4069206420210025
Paper number - 208
Paper name - Comparative Literature & Translation Studies
Subject Code - 22415
Origin of the word Plagiarism
According to the Marriam Webster Dictionary, The word Plagiarize or plagiarism comes from the Latin word plagiarius, which means “kidnapper.”
The word plagiarism has an interesting origin that can be traced back to the Latin word "plagiarius." In its original meaning, "plagiarius" referred to a kidnapper or someone who abducted a person. The word "plaga" meant a type of net that hunters used to catch game, and eventually, "plagiarius" was extended to include someone who stole words, rather than people, from another.
As the word evolved over time and made its way into the English language, it retained its original reference to kidnapping. When the word was first used in English, it appeared as "plagiary," which was used to describe someone who had committed literary theft or stolen someone else's ideas.
Over time, the term "plagiarism" became more commonly used, and it is now widely recognized as a serious offense in academic and professional circles. In today's society, plagiarism is viewed as a form of intellectual theft that can have serious consequences, including damaged reputations, loss of credibility,and legal repercussions.
The origin of the word plagiarism offers a fascinating glimpse into the history of language and the ways in which words evolve and change over time. While the word may have started out as a reference to kidnapping, its meaning has shifted over the centuries, and it now serves as a warning to writers and thinkers everywhere to be diligent in their efforts to produce original work.
What is Plagiarism?
As per Plagiarism in Research — The Complete Guide [eBook] by DEEPTANSHU D plagiarism is representing a part of or the entirety of someone else's work as your own. Whether published or unpublished, this could be ideas, text verbatim, infographics, etc.
Website of Oxford Student says that, Plagiarism is presenting work or ideas from another source as your own, with or without consent of the original author, by incorporating it into your work without full acknowledgement.
According to Scribbr, Plagiarism means using someone else’s work without giving them proper credit. In academic writing, plagiarizing involves using words, ideas, or information from a source without citing it correctly.
According to Oxford Dictionary plagiarism is the practice of taking someone else's work or ideas and passing them off as one's own.
MLA Handbook for writers of Research Papers noted that, Plagiarism involves two kinds of wrongs, using another person's ideas, information, or expressions without acknowledging that person's work constitutes intellectual theft. Passing off another person’s ideas, information, or expression as your own to get a better grade or gain some other advantage constitutes fraud.
Plagiarism is sometimes a moral and ethical offence rather than a legal one since some instances of plagiarism fall outside the scope of copyright infringement, a legal offense.
Forms of Plagiarism
Here are some forms of plagiarism given in MLA Handbook for Writers of Research Papers (Seventh Edition).
1] Repeating or Paraphrasing Wording :
Repeating or paraphrasing wording is a form of plagiarism that occurs when a writer copies or restates someone else's words or ideas without proper citation. This type of plagiarism can take many forms, such as directly copying and pasting text, paraphrasing sentences or ideas without attribution, or using synonyms to replace key words while retaining the original structure and meaning of the text.For example,
Original Source : Someone is using information about Dickinson’s poems that appears on page 625 of an essay by Wendy Martin in the book Columbia Literary History of the United States.
Plagiarism : Emily Dickinson Firmly Believe that….
Without Plagiarism : As Wendy Martin has suggested, Emily Dickinson firmly believed that….
In the example provided, the writer has committed plagiarism by paraphrasing the information about Dickinson's poems without citing the original source. Instead of acknowledging Wendy Martin's essay as the source of the information, the writer presents it as their own idea, using different wording but retaining the same meaning.
To avoid this type of plagiarism, it is important to properly cite all sources and use your own words to express ideas and arguments. When taking notes or researching, be sure to record the source of all information and paraphrase it in your own words while still giving credit to the original source. Additionally, when using direct quotes or paraphrasing, use quotation marks and provide a citation for the original source to avoid plagiarism.
Thus, repeating or paraphrasing wording plagiarism involves copying or restating someone else's words or ideas without proper citation or attribution, and it is important to take steps to avoid this type of plagiarism in all writing endeavors.
2] Taking a particularly Apt Phrase
Taking a particularly apt phrase is a form of plagiarism that occurs when a writer uses a phrase or concept that was invented or popularized by someone else without proper citation. This type of plagiarism can be particularly subtle, as the writer may not realize that the phrase they are using was not their own creation. For example,
Original Source : Everyone uses the word language and everybody these days talks about culture… “Languaculture” is a reminder….(Michael Agar, Language Shock: Understanding the Culture of Conversation[New York: Morrow, 1994;60])
Plagiarism : At the intersection of language and culture lies a concept that we might call “Languaculture”.
Without Plagiarism : At the intersection of language and culture lies a concept that Michael Agar has called “Languaculture” (60).
In the example provided, the writer has committed plagiarism by using the term "Languaculture" without giving proper credit to Michael Agar, who coined the term in his book Language Shock: Understanding the Culture of Conversation. By presenting the term as their own idea, the writer is taking credit for Agar's original contribution to the field of language and culture studies.
To avoid this type of plagiarism, it is important to properly cite all sources and give credit to the original creator of any particularly apt phrase or concept. In the example provided, the writer could have avoided plagiarism by acknowledging Agar's contribution and using his exact wording, as shown in the "Without Plagiarism" version of the sentence.
Plagiarism in Research — The Complete Guide [eBook] includes some forms of plagiarism.
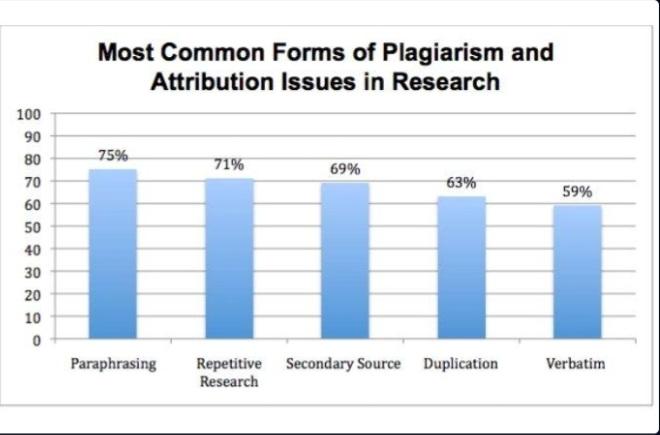
3] Global or Complete Plagiarism
Global or complete plagiarism is a form of intellectual theft that involves copying an entire work, without giving proper attribution to the original author. This type of plagiarism can occur in various forms, including copying a book, article, research paper, or even a website. In essence, it is an act of claiming someone else's intellectual property as one's own without any acknowledgment or consent.
Global plagiarism is a serious offense and is considered a violation of copyright laws, which protect the rights of original creators. When an individual is caught engaging in this type of plagiarism, they can face legal action, fines, or even imprisonment,depending on the severity of the offense and the country's laws. Additionally, global plagiarism can also damage an individual's reputation, as it is a clear indication of dishonesty and lack of academic integrity.
One of the main reasons why global plagiarism occurs is due to a lack of understanding of what constitutes plagiarism and the importance of proper citation. Some individuals may be under the impression that copying a work verbatim is acceptable, especially if they are pressed for time or lack the necessary skills to create an original work. However, this is not the case, as even paraphrasing or summarizing someone else's work without proper attribution can also be considered plagiarism.
To avoid global plagiarism, it is essential to give credit where credit is due. This means citing all sources used in a work and acknowledging the original author's contribution to the field. Additionally, individuals can use plagiarism detection tools to check their work for any instances of unintentional plagiarism. Overall, global plagiarism is a serious offense that can have severe consequences and should be avoided at all costs.
4] Verbatim or Direct Plagiarism
According to Plagiarism in Research — The Complete Guide [eBook], this type of Plagiarism happens when someone copy a part of someone else's work, word-to-word, without providing adequate credits or attributions.
Verbatim or direct plagiarism is a form of plagiarism in which an individual copies a part of someone else's work word-for-word without giving proper attribution or citation. In other words, verbatim plagiarism occurs when an individual reproduces an exact sentence or passage from an original source without putting it in quotation marks or acknowledging the original author.
This type of plagiarism can happen intentionally or unintentionally, but in either case, it is a serious offense that can result in legal action and damage to the individual's reputation. Verbatim plagiarism is particularly concerning in research and academic writing, where originality and integrity are essential.
To avoid verbatim plagiarism, it is important to use proper citation and attribution. Whenever an individual uses someone else's words or ideas, they should put them in quotation marks and provide a proper citation, including the author's name, the title of the work, and the page number. Paraphrasing or summarizing someone else's work without proper citation can also be considered verbatim plagiarism if the ideas and structure of the original work are replicated.
One way to avoid verbatim plagiarism is to use plagiarism detection tools, which can identify similarities between an individual's work and other sources. However, it is important to note that these tools are not foolproof and should be used as a complement to proper citation and attribution.
5] Source-based Plagiarism
As per Plagiarism in Research — The Complete Guide [eBook], this type of plagiarism happens when someone tries to mislead or disguise the natural source of their work.
Source-based plagiarism occurs when someone directly copies words, phrases, sentences, or ideas from a source without giving proper attribution or citation. In other words, it is a type of plagiarism where the author uses someone else's work without acknowledging it.
There are various forms of source-based plagiarism, such as verbatim copying, paraphrasing without attribution, and improper citation. Verbatim copying is the most obvious form of plagiarism, where someone copies the exact words from a source and presents them as their own. Paraphrasing without attribution is a more subtle form of plagiarism, where the author rephrases the original text in their own words but fails to give credit to the original author.
Improper citation is another form of source-based plagiarism, where the author cites a source but fails to follow the correct citation format or omits important details, such as the page number or publication date. This can make it difficult for readers to verify the accuracy of the information or locate the original source.
Source-based plagiarism is a serious ethical and academic offense that can have severe consequences, including academic penalties, damage to reputation, and legal action. To avoid source-based plagiarism, it is important to always give proper attribution and citation to any sources used in your work. This includes both direct quotes and paraphrased information. When in doubt, it is better to err on the side of caution and provide more information rather than less.
6] Ghostwriting
Ghostwriting is a type of plagiarism that occurs when someone hires another person to write, edit or proofread their work without giving any credit or acknowledgement. In other words, ghostwriting is when someone else writes the work and the original author passes it off as their own.
This kind of plagiarism raises serious questions about the academic capabilities of the author because it suggests that they are not able to write their own work, and therefore, are not deserving of the credit or recognition that comes with it. Ghostwriting is particularly common in academic and professional settings, where authors may not have the time or skills to complete the work on their own.
While there are some legitimate reasons for using a ghostwriter, such as when a public figure wants to write a book but doesn't have the time or writing ability, it is important for the author to acknowledge the ghostwriter's contributions to the work. Otherwise, it is considered plagiarism and can lead to serious consequences such as loss of credibility, legal action, and even job loss.
In conclusion, ghostwriting is a type of plagiarism that occurs when someone hires someone else to write, edit or proofread their work without giving them credit. It raises serious questions about the academic abilities of the author and can have serious consequences if discovered.
7] Self-plagiarism
Self-plagiarism refers to the act of reusing one's own previously published or submitted work without proper citation or attribution. Even though the author may own the copyright to their work, they cannot reuse the same work in its entirety or significant portions of it without proper citation.
Self-plagiarism can occur in various forms, such as submitting a previously published paper as new work, recycling sections of a previous manuscript without proper citation, or using the same data to support multiple publications without acknowledging the earlier work.
The primary concern with self-plagiarism is that it misrepresents the amount of original work the author has done. It can also be seen as an attempt to inflate the author's publication record or to present a more impressive academic profile. It is also considered unethical because it is an attempt to gain credit for work that has already been recognized or rewarded.
Therefore, it is important for authors to be aware of the potential for self-plagiarism and take steps to avoid it, such as proper citation and attribution of their own work.
8] Accidental Plagiarism
Accidental plagiarism refers to the unintentional act of presenting someone else's work or ideas as your own. It often happens when one is not careful while using sources and forgets to include proper citations. This can occur through unwitting paraphrasing, missing in-text or end-of-text citations, or not using quotation blocks.
Accidental plagiarism can result in serious consequences, including loss of reputation, damaged academic integrity, and even legal actions. However, it is usually considered less severe than intentional plagiarism. To avoid accidental plagiarism, it is essential to proofread carefully and make sure that all sources are appropriately cited. One can also use plagiarism detection software to check their work for any possible instances of plagiarism. By taking these steps, one can ensure that they are giving credit to the original sources and avoiding any form of plagiarism.
Conclusion
In conclusion, plagiarism is a serious offense in academic and professional settings. It can take various forms, such as verbatim plagiarism, mosaic plagiarism, self-plagiarism, source-based plagiarism, ghostwriting, and accidental plagiarism. Each form of plagiarism poses a threat to the originality and integrity of one's work and can result in severe consequences, including loss of credibility, legal action, and academic or professional penalties. Therefore, it is essential to understand and avoid all forms of plagiarism by properly citing and acknowledging sources, utilizing effective research and writing strategies, and utilizing plagiarism detection tools when necessary.
Work Cited
Deeptanshu D, and Dogra Shubham. “What Is Plagiarism? - The Complete Guide [Ebook]” SciSpace, SciSpace Resources, 18 Oct. 2022,https://typeset.io/resources/the-only-plagiarism-guide-you-will-need/.
Gibaldi, Joseph. MLA Handbook for Writers of Research Papers. Seventh ed., Modern Language Association of America, 2015.
Hornby, Albert Sydney. Oxford Advanced Learner's Dictionary of Current English / [by] A.S. Hornby ; Editor Jonathan Crowther. Oxford, England :Oxford University Press, 1995.
“Plagiarism.” Merriam-Webster.com Dictionary, Merriam-Webster, https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/plagiarism.
"Plagiarism." University of Oxford, 2023, https://www.ox.ac.uk/students/academic/guidance/skills/plagiarism.
Scribbr. “What Is Plagiarism? | Definition and Examples.” Scribbr, www.scribbr.com/category/plagiarism.



.png)


